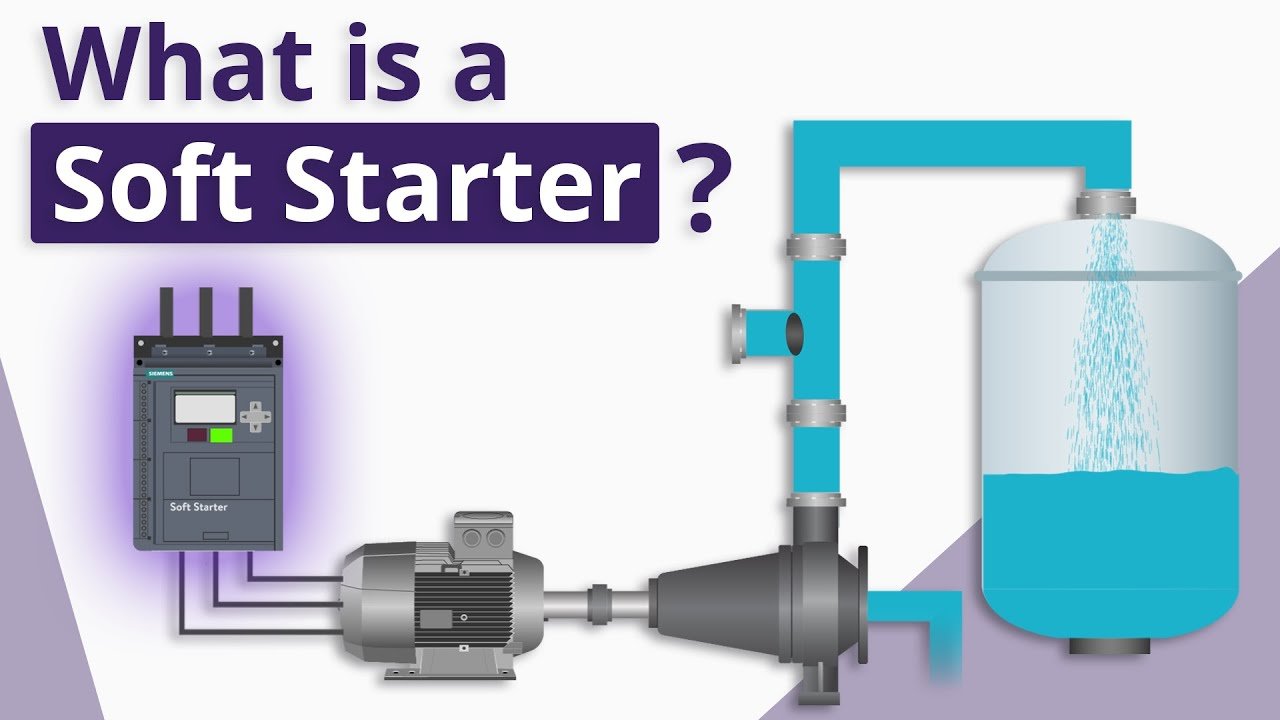
Motor Soft Starter: What Is It and How Does It Work?
A Motor Soft Starter is an electrical device used to control the acceleration and deceleration of electric motors, reducing mechanical stress and preventing electrical surges. Unlike traditional direct-on-line (DOL) starters, soft starters gradually ramp up voltage to minimize inrush current and torque shock. They are widely used in various industrial applications, improving efficiency, reliability, and lifespan of electric motors.
Types of Motor Soft Starters
Motor soft starters can be categorized based on voltage levels, control mechanisms, and applications. The two primary types are:
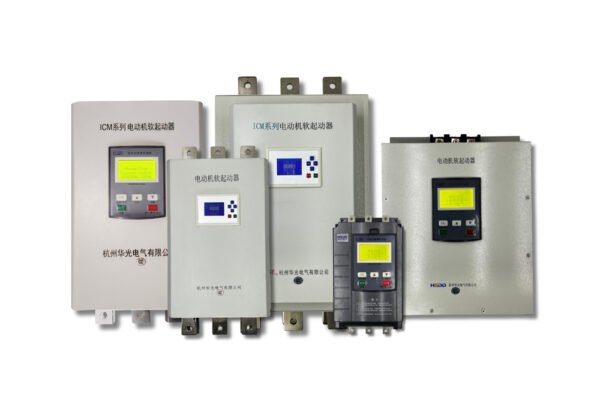
1. Low Voltage Soft Starter (LVSS)
Low Voltage Soft Starters are designed for motors operating below 1000V. These are commonly used in commercial and industrial applications where motors require smooth starts and controlled acceleration.
Key Features of Low Voltage Soft Starters:
- Voltage range: Typically 200V to 690V
- Reduced mechanical stress on motor components
- Protection against overheating and overcurrent
- Integration with industrial automation systems
Common Applications:
- HVAC systems
- Pumps and compressors
- Conveyor belts
- Fans and blowers
LTICM Series Low-voltage Motor Soft Starter
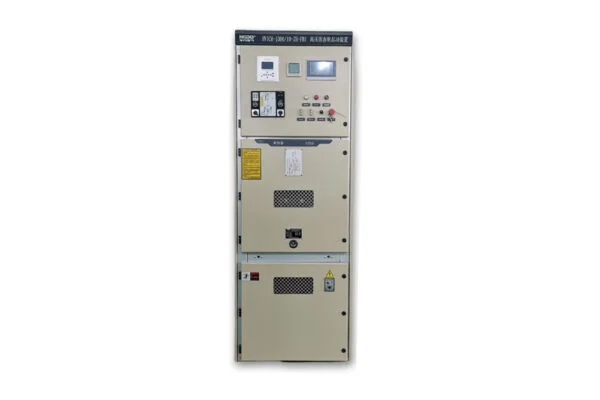
2. High Voltage Soft Starter (HVSS)
High Voltage Soft Starters are used for motors operating above 1000V, typically in heavy industries requiring higher power and torque. These starters are built to handle more demanding applications with greater protection mechanisms.
Key Features of High Voltage Soft Starters:
- Voltage range: 1000V to 15kV
- Advanced motor protection and fault diagnostics
- Lower electrical stress and heat generation
- Increased energy efficiency
Common Applications:
- Mining and drilling equipment
- Large industrial compressors
- Oil and gas industry pumps
- High-power fans and turbines
HVLTICM Series High-voltage Motor Solid State Soft Starter
How Does a Motor Soft Starter Work?
A Motor Soft Starter gradually increases the voltage supplied to the motor during startup, thereby reducing inrush current and mechanical stress. It operates in three main phases:
1. Ramp-Up (Acceleration Phase)
- Voltage is gradually increased
- Motor speed smoothly increases
- Reduces mechanical shocks and prevents sudden torque spikes
2. Steady-State Operation
- Motor runs at full voltage after startup
- Soft starter may remain active for monitoring and protection
3. Ramp-Down (Deceleration Phase)
- Controlled reduction in voltage
- Helps prevent sudden stops and mechanical stress
- Useful in conveyor systems, pumps, and other inertia-sensitive applications
Advantages of Using a Motor Soft Starter
✔ Reduced Electrical and Mechanical Stress – Prevents damage to motors, shafts, and connected equipment.
✔ Energy Efficiency – Minimizes power surges and optimizes motor performance.
✔ Extended Motor Lifespan – Reduces wear and tear by avoiding sudden voltage spikes.
✔ Improved Process Control – Provides smooth and stable motor operation, especially in conveyor and pump applications.
✔ Enhanced Protection Features – Protects against overheating, overcurrent, phase loss, and voltage fluctuations.
Comparison: Motor Soft Starter vs. Variable Frequency Drive (VFD)
| Feature | Motor Soft Starter | Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Smooth motor startup | Full speed control of motor |
| Speed Control | No (only controls starting & stopping) | Yes (adjustable speed during operation) |
| Energy Savings | Limited (only at startup) | High (adjusts speed to demand) |
| Complexity | Simple | More complex |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Applications | Pumps, conveyors, fans | Applications requiring speed variation |
Common Questions About Motor Soft Starters
1. What is the difference between a soft starter and a VFD?
A soft starter only manages motor startup and shutdown, while a VFD provides continuous speed control throughout operation.
2. Can a motor soft starter save energy?
Yes, it reduces inrush current and prevents energy spikes, although it does not provide the same level of energy savings as a VFD.
3. Do soft starters work with all motor types?
Soft starters are primarily designed for AC induction motors. Compatibility with other motor types depends on the specific application.
4. Are soft starters necessary for all motors?
Not all motors require a soft starter. They are mainly used for large motors that need controlled acceleration to prevent damage and electrical disturbances.
5. How do I choose the right motor soft starter?
Consider factors such as motor voltage, current rating, application requirements, protection features, and environmental conditions when selecting a motor soft starter.
Final Thoughts
A Motor Soft Starter is an essential component in industrial motor control, providing smooth motor operation while protecting equipment from electrical and mechanical stress. Whether for low-voltage soft starter or high-voltage soft starter applications, selecting the right soft starter can significantly enhance motor efficiency and system reliability.
By implementing motor soft starters, businesses can reduce downtime, optimize energy consumption, and extend the lifespan of their motors, making them a valuable investment in industrial automation.
Author Profile
Latest entries
 IoT2025-04-14Electrical Automation – The Indispensable Behind-the-Scenes Hero of the Internet of Things
IoT2025-04-14Electrical Automation – The Indispensable Behind-the-Scenes Hero of the Internet of Things Electrical Automation Knowledge2025-04-11Electrical Automation Solutions in the Energy Storage Industry: Applications, Advancements, and Benefits
Electrical Automation Knowledge2025-04-11Electrical Automation Solutions in the Energy Storage Industry: Applications, Advancements, and Benefits Electrical Safety & Protection2025-04-06Electric Motor Protection and Control Systems: An In-depth Overview
Electrical Safety & Protection2025-04-06Electric Motor Protection and Control Systems: An In-depth Overview Electrical Automation Knowledge2025-04-01The Application of Electrical Automation in the New Energy Industry
Electrical Automation Knowledge2025-04-01The Application of Electrical Automation in the New Energy Industry












